- IPSec Support Pages
- Configuring Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Over .. - Cisco
- Cisco Vpn L2tp Over Ipsec
- Configuring IPSec Network Security
- Configuring L2TP Over IPSec VPN On Cisco ASA – IT Network ..
- Cisco Anyconnect L2tp
- See full list on cisco.com.
- VPN NINJA offers the VPN connection with Japan. A VPN protocol is Cisco AnyConnect,OPENVPN,PPTP,L2TP,SSTP,IPSec,IKEv2 and PacketiX VPN.
- Cisco L2TPv3/IPsec Edge-VPN Router Setup Most of Cisco's routers which are released on or after 2005 has L2TPv3 over IPsec protocol function. (If not, you might be able to upgrade the IOS version to support it.).
- Allow leasing IP address from Radius server for L2TP, PPTP and CISCO VPN Client Click to lease the IP address to the L2TP, PPTP and CISCO VPN client users through the Radius server. Radius is a protocol that allows network devices to authenticate users against a central database.
This page provides instructions for configuring client VPN services through the Dashboard.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a VPN tunneling protocol that allows remote clients to use the public. Such as Cisco VPN client software, is required. Note L2TP over IPsec supports only IKEv1. IKEv2 is not supported. MAC OS X, Android, and Cisco IOS. Only L2TP with IPsec is supported, native L2TP itself is not supported on ASA.
For detailed instructions on how to configure a client VPN connection on various client device platforms, please refer to:
Client VPN
The client VPN service uses the L2TP tunneling protocol and can be deployed without any additional software on PCs, Macs, iOS devices, and Android devices, since all of these operating systems natively support L2TP VPN connections.
Note: TLS (SSL) Client VPN is supported on the MX with AnyConnect. To learn more, see AnyConnect on the MX
Note: Linux-based operating systems can support client VPN connections as well, although third-party packages may be necessary to support L2TP/IP.
Free download program treasury integrated software programs. Note: Establishing a client VPN connection when the client is located on the LAN of the MX is unsupported.
Encryption Method
Client VPN uses the L2TP/IP protocol, with the following encryption and hashing algorithms: 3DES and SHA1 for Phase1, AES128/3DES and SHA1 for Phase2. As a best practice, the shared secret should not contain any special characters at the beginning or end.
Owing to changes in the PCI-DSS Standard version 3.2.1, some auditors are now enforcing requirements for stronger encryption than the Meraki Client VPN default settings provide. Please contact Meraki Support if you need these values adjusted, but please be aware that some client devices may not support these more stringent requirements (AES128 encryption with DH group 14 - Required by PCI-DSS 3.2.1).
Client VPN Server Settings
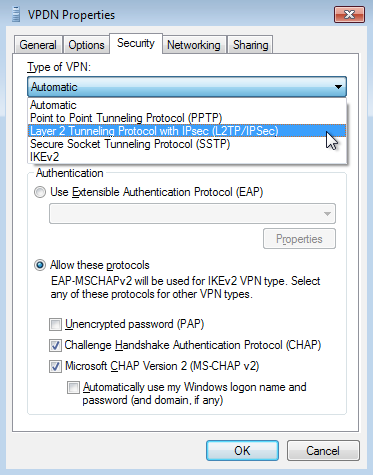
To enable Client VPN, choose Enabled from the Client VPN server pulldown menu on the Security Appliance > Configure > Client VPN page. The following Client VPN options can be configured:
- Client VPN Subnet: The subnet that will be used for Client VPN connections. This should be a private subnet that is not in use anywhere else in the network. The MX will be the default gateway on this subnet and will route traffic to and from this subnet.
- Hostname: This is the hostname of the MX that Client VPN users will use to connect. This hostname is a DDNS host record correlating to the Public IP address of the MX. You can change this hostname by following the instructions here.
- DNS server: The servers VPN Clients will use to resolve DNS hostnames. Chose from Google Public DNS, OpenDNS, or specifying custom DNS servers by IP address.
- WINS server: If VPN clients should use WINS to resolve NetBIOS names, select Specify WINS Servers from the drop-down and enter the IP addresses of the desired WINS servers.
- Shared secret: The shared secret that will be used to establish the Client VPN connection.
- Authentication: How VPN Clients will be authenticated (see below).
- Systems Manager Sentry VPN security: Configuration settings for whether devices enrolled in systems manager should receive a configuration to connect to the Client VPN (see below Systems Manager Sentry VPN Security section).
Authentication
Meraki Client VPN uses the Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) to transmit and authenticate credentials. PAP authentication is always transmitted inside an IPsec tunnel between the client device and the MX security appliance using strong encryption. User credentials are never transmitted in clear text over the WAN or the LAN. An attacker sniffing on the network will never see user credentials because PAP is the inner authentication mechanism used inside the encrypted IPsec tunnel.
The authentication itself can be performed by using these three options: the Meraki cloud, RADIUS, or Active Directory. Below, the three options are discussed.
Meraki Cloud Authentication
Use this option if an Active Directory or RADIUS server is not available, or if VPN users should be managed via the Meraki cloud. To add or remove users, use the User Management section at the bottom of the page. Add a user by clicking 'Add new user' and entering the following information:
- Name: Enter the user's name.
- Email: Enter the user's email address.
- Password: Enter a password for the user or click 'Generate' to automatically generate a password.
- Authorized: Select whether this user is authorized to use the Client VPN.
To edit an existing user, click on the user under the User Management section. To delete a user, click the X next to the user on the right side of the user list.
When using Meraki hosted authentication, the user's email address is the username that is used for authentication.
RADIUS

Use this option to authenticate users on a RADIUS server. Click Add a RADIUS server to configure the server(s) to use. Enter in the IP address of the RADIUS server, the port to be used for RADIUS communication, and the shared secret for the RADIUS server.
For more information on how to configure Radius authentication for Client VPN, refer to the documentation on Configuring RADIUS Authentication with Client VPN.
Note: If multiple RADIUS servers are configured, RADIUS traffic will not be load balanced.
Active Directory
Use this option if user authentication should be done with Active Directory domain credentials. You will need to provide the following information:
- Short domain: The short name of the Active Directory domain.
- Server IP: The IP address of an Active Directory server on the MX LAN or a remote subnet routable through AutoVPN.
- Domain admin: The domain administrator account the MX should use to query the server.
- Password: Password for the domain administrator account.
For example, considering the following scenario: Users in the domain test.company.com should be authenticated using an Active Directory server with IP 172.16.1.10. Users normally log into the domain using the format 'test/username' and you have created a domain administrator account with the username 'vpnadmin' and the password 'vpnpassword'.
- The Short domain would be 'test'.
- The Server IP would be 172.16.1.10.
- The Domain admin would be 'vpnadmin'.
- The Password would be 'vpnpassword'.
Refer to the Active Directory documentation for more information about integrating AD with Client VPN.
Note: At this time, the MX does not support mapping group policies via Active Directory for users connecting through the Client VPN.
Systems Manager Sentry VPN Security
When using Meraki cloud authentication, Systems Manager Sentry VPN security can be configured If your Dashboard organization contains one or more MDM networks. Systems Manager Sentry VPN security allows for devices enrolled in Systems Manager to receive the configuration to connect to the Client VPN through the Systems Manager profile on the device.
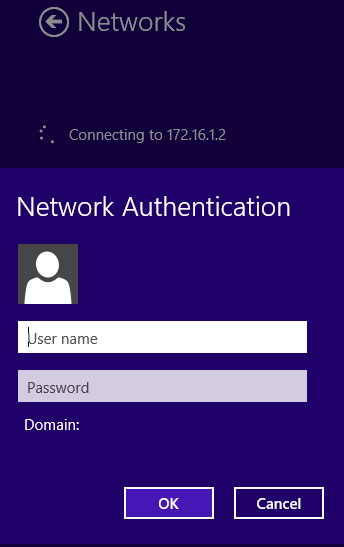
To enable Systems Manager Sentry VPN security, choose Enabled from the Client VPN server pulldown menu on the Security Appliance > Configure > Client VPN page. You can configure the following options:
- Install Scope: The install scope allows for a selection of Systems Manager tags for a particular MDM network. Devices with these tags applied in a Systems Manager network will receive a configuration to connect to this network's Client VPN server through their Systems Manager profile.
- Send All Traffic: Select whether all client traffic should be sent to the MX.
- Proxy: Whether a proxy should be used for this VPN connection. This can be set to automatic, manual, or disabled
When using Systems Manager Sentry VPN security, the username and password used to connect to the client VPN are generated by the Meraki cloud.
Usernames are generated based on a hash of a unique identifier on the device and the username of that device. Passwords are randomly generated.
Client VPN Connections
After configuring Client VPN and users are starting to connect, it may be useful to see how many and what client devices are connected to your network via Client VPN. To see connected Client VPN devices, navigate to Network-wide > Clients > click the dropdown icon on the Search clients.. search bar > make sure to select Client VPN and either Online, Offline or both.
Group Policies
It is possible to manually apply group policies to clients connected via Client VPN. Group Policy applied to a client VPN user is associated with the username and not the device. Different devices that connect to Client VPN with the same username will receive the same group policy. For more help on assigning or removing group policies applied to a client, refer to the Creating and Applying Group Policies document.
IPSec Support Pages
Note: It is not possible to assign group policies automatically once a user connects to Client VPN.
FAQs Page
If further guidance is required, please feel free to visit the FAQs page built into Client VPN page (Security Appliance > Configure > Client VPN > FAQs). The FAQs contain answers and links (KB Articles and Dashboard pages) to the most common Client VPN inquiries. Below is a snippet of the FAQs page.
Contents
Introduction
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) over IPSec provides the capability to deploy and administer an L2TP VPN solution alongside the IPSec VPN and firewall services in a single platform. The primary benefit of the configuration of L2TP over IPSec in a remote access scenario is that remote users can access a VPN over a public IP network without a gateway or a dedicated line, which enables remote access from virtually any place with plain old telephone service (POTS). An additional benefit is that the only client requirement for VPN access is the use of Windows with Microsoft Dial-Up Networking (DUN). No additional client software, such as the Cisco VPN client software, is required.
This document provides a sample configuration for the native L2TP/IPSec Android client. It takes you through all the necessary commands required on a Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA), as well as the steps to be taken on the Android device itself.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the following software and hardware versions:
- Android L2TP/IPSec requires Cisco ASA software version 8.2.5 or later, version 8.3.2.12 or later, or version 8.4.1 or later.
- ASA supports Secure Hash Algorithm 2 (SHA2) certificate signature support for Microsoft Windows 7 and Android-native VPN clients when the L2TP/IPSec protocol is used.
- See Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI, 8.4 and 8.6: Configuring L2TP over IPSec: Licensing Requirements for L2TP over IPSec.
The information in this document was created from devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command. Duct sizing chart free download.
Configure
This section describes the information one would need in order to configure the features described in this document.
Configure the L2TP/IPSec Connection on the Android
Configuring Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Over .. - Cisco
This procedure describes how to configure the L2TP/IPSec connection on the Android:
- Open the menu, and choose Settings.
- Choose Wireless and Network or Wireless Controls. The available option depends on your version of Android.
- Choose VPN Settings.
- Choose Add VPN.
- Choose Add L2TP/IPsec PSK VPN.
- Choose VPN Name, and enter a descriptive name.
- Choose Set VPN Server, and enter a descriptive name.
- Choose Set IPSec pre-shared key.
- Uncheck Enable L2TP secret.
- [Optional] Set the IPSec identifier as the ASA tunnel group name. No setting means it will fall into DefaultRAGroup on the ASA.
- Open the menu, and choose Save.
Configure the L2TP/IPSec Connection on ASA
These are the required ASA Internet Key Exchange Version 1 (IKEv1) (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol [ISAKMP]) policy settings that allow native VPN clients, integrated with the operating system on an endpoint, to make a VPN connection to the ASA when L2TP over IPSec protocol is used:
Cisco Vpn L2tp Over Ipsec
- IKEv1 phase 1 - Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) encryption with SHA1 hash method
- IPSec phase 2 - 3DES or Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption with Message Digest 5 (MD5) or SHA hash method
- PPP Authentication - Password Authentication Protocol (PAP), Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol version 1 (MS-CHAPv1), or MS-CHAPv2 (preferred)
- Pre-shared key
Note: The ASA supports only the PPP authentications PAP and MS-CHAP (versions 1 and 2) on the local database. The Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) and CHAP are performed by proxy authentication servers. Therefore, if a remote user belongs to a tunnel group configured with the authentication eap-proxy or authentication chap commands and if the ASA is configured to use the local database, that user will be unable to connect.
Furthermore, Android does not support PAP and, because Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) does not support MS-CHAP, LDAP is not a viable authentication mechanism. The only workaround is to use RADIUS. See Cisco Bug ID CSCtw58945, 'L2TP over IPSec connections fail with ldap authorization and mschapv2,' for further details on issues with MS-CHAP and LDAP.
This procedure describes how to configure the L2TP/IPSec connection on the ASA:
- Define a local address pool or use a dhcp-server for the adaptive security appliance in order to allocate IP addresses to the clients for the group policy.
- Create an internal group-policy.
- Define the tunnel protocol to be l2tp-ipsec.
- Configure a domain name server (DNS) to be used by the clients.
- Create a new tunnel group or modify the attributes of the existing DefaultRAGroup. (A new tunnel group can be used if the IPSec identifier is set as group-name on the phone; see step 10 for the phone configuration.)
- Define the general attributes of the tunnel group that are used.
- Map the defined group policy to this tunnel group.
- Map the defined address pool to be used by this tunnel group.
- Modify the authentication-server group if you want to use something other than LOCAL.
- Define the pre-shared key under the IPSec attributes of the tunnel group to be used.
- Modify the PPP attributes of the tunnel group that are used so that only chap, ms-chap-v1 and ms-chap-v2 are used.
- Create a transform set with a specific encapsulating security payload (ESP) encryption type and authentication type.
- Instruct IPSec to use transport mode rather than tunnel mode.
- Define an ISAKMP/IKEv1 policy using 3DES encryption with SHA1 hash method.
- Create a dynamic crypto map, and map it to a crypto map.
- Apply the crypto map to an interface.
- Enable ISAKMP on that interface.
Configuration File Commands for ASA Compatibility
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) in order to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
This example shows the configuration file commands that ensure ASA compatibility with a native VPN client on any operating system.
Configuring IPSec Network Security
ASA 8.2.5 or Later Configuration Example

ASA 8.3.2.12 or Later Configuration Example
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
This procedure describes how to set up the connection:
- Open the menu, and choose Settings.
- Select Wireless and Network or Wireless Controls. (The available option depends on your version of Android.)
- Select the VPN configuration from the list.
- Enter your username and password.
- Select Remember username.
- Select Connect.
This procedure describes how to disconnect:
- Open the menu, and choose Settings.
- Select Wireless and Network or Wireless Controls. (The available option depends on your version of Android.)
- Select the VPN configuration from the list.
- Select Disconnect.
Use these commands in order to confirm that your connection works properly.
Configuring L2TP Over IPSec VPN On Cisco ASA – IT Network ..
- show run crypto isakmp - For ASA version 8.2.5
- show run crypto ikev1 - For ASA version 8.3.2.12 or later
- show vpn-sessiondb ra-ikev1-ipsec - For ASA version 8.3.2.12 or later
- show vpn-sessiondb remote - For ASA version 8.2.5
Note: The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) supports certain show commands. Use the Output Interpreter Tool in order to view an analysis of show command output.
Known Caveats
- Cisco bug ID CSCtq21535, 'ASA traceback when connecting with Android L2TP/IPsec client'
- Cisco bug ID CSCtj57256, 'L2TP/IPSec connection from Android doesn't establish to the ASA55xx'
- Cisco bug ID CSCtw58945, 'L2TP over IPSec connections fail with ldap authorization and mschapv2'
Cisco Anyconnect L2tp
Related Information
